Overlooking ADA toilet requirements can result in costly fines, lawsuits, and unsafe spaces for millions with disabilities, putting architects and contractors at risk of legal pitfalls. With mandates for precise heights and clearances, non-compliance often leads to accessibility barriers that affect daily use in commercial buildings.
This guide breaks down essential ADA toilet standards—covering heights of 17-19 inches, minimum 60-inch front clearances, and secure grab bar placements—to help you design compliant, user-friendly restrooms. By focusing on these details, you’ll avoid common errors and ensure safer, legally sound facilities for everyone.
Introduction to ADA Toilet Requirements
The Americans with Disabilities Act, or ADA, sets important rules for making bathrooms accessible to everyone, especially people with disabilities. This means designing toilets that are easy to use and safe, which helps avoid accidents and ensures fairness in public places. Understanding ADA toilet standards can make a big difference in commercial buildings, like stores or offices, where everyone needs to feel welcome and secure.
First off, the ADA is a federal law from 1990 that protects people with disabilities by requiring certain features in public spaces. When it comes to toilet design, this includes things like the right height and space so wheelchairs can fit comfortably. For instance, an ADA-compliant toilet must meet specific guidelines to prevent exclusion and promote independence, making daily life smoother for millions of Americans.
Why does ADA compliance matter so much in commercial building design? Well, it’s not just about following the law to avoid fines; it’s about creating safer environments that boost customer satisfaction and reduce risks. Buildings that ignore these standards might face lawsuits or costly changes later, while compliant ones build trust and accessibility. Plus, using ADA-compliant fixtures can even lower long-term maintenance costs by focusing on durable, user-friendly designs.
Let us dive into the key takeaways on height, space, and accessibility features for an ADA toilet. The standard height for an ADA-compliant toilet is usually between 17 and 19 inches from the floor to the seat, allowing easier access for those in wheelchairs. You also need at least 60 inches of clear space in front of the toilet and 56 inches on the side for maneuvering, which helps with safety and usability. Other features include grab bars placed 33 to 36 inches above the floor and easy-to-use flush handles, all aimed at preventing falls and ensuring comfort.
One common challenge in implementing ADA standards is retrofitting older buildings, which often involves structural changes that can be pricey and complex. For example, adding the required space might mean knocking down walls or rearranging plumbing, leading to unexpected delays and costs. Despite these hurdles, planning ahead with certified suppliers can make the process smoother, offering products that align with ADA guidelines without cutting corners.
Working with reliable sources for ADA toilet fixtures is key to success in commercial projects. Companies like Foshan Seletti provide water closet options that match general standards, helping buyers find cost-effective solutions that fit budgets while ensuring quality. This approach not only meets legal needs but also supports efficient procurement, saving time and reducing waste in the long run. By choosing the right partners, businesses can handle these requirements with less stress and more confidence.
Common challenges also include staying up-to-date with evolving ADA rules, as guidelines can change over time based on new technology or feedback. Another issue is balancing aesthetics with functionality, where designers must ensure stylish toilets still meet accessibility criteria. Overcoming these involves regular training and consultations to keep everything in check, turning potential problems into opportunities for better design.
When it comes to ADA toilet height requirements, precision is everything to avoid non-compliance. The space needed for ADA-compliant toilets often requires careful measurements to fit into existing layouts without major overhauls. These details might seem small, but they play a big role in creating inclusive spaces that work for all users.
A hidden insight is that while new constructions can easily incorporate ADA standards, retrofitting old spaces brings extra costs and structural headaches. This underscores the need for long-term strategies, like regular maintenance checks, to keep facilities adaptable over time. By addressing these early, property owners can avoid bigger issues down the road and promote a more inclusive environment.
Focusing on ADA toilet guidelines helps ensure buildings are accessible and safe, supporting legal compliance while improving user experiences for everyone involved.
ADA Toilet Specification Overview
| Requirement Type | Minimum Height (inches) | Minimum Space (inches) | Key Accessibility Features | Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toilet Seat | 17 | 60 in front | Grab bars required | Measured from floor; ensures easy transfer |
| Flush Valve | N/A | 56 on side | Easy lever operation | Must be operable with one hand; reduces strain |
| Clear Floor Space | N/A | 48 x 60 overall | Wheelchair maneuverability | Allows 360-degree turn; based on ADAAG standards |
| Grab Bar Placement | 33-36 from floor | 42 in length | 1.5-inch diameter | Supports up to 250 lbs; prevents slips |
| Door Clearance | N/A | 32 wide | Out-swinging doors | Facilitates entry; measured per ADA guidelines |
In summary, getting ADA toilet setups right involves blending practical design with regulatory knowledge to foster accessibility. This not only aids in legal compliance but also enhances daily use for people with disabilities. As you move forward, remember these basics can guide better decisions in your projects.


Understanding Key Dimensions and Height Specifications
The ADA sets clear standards for toilet dimensions to make bathrooms safer and more usable for everyone, especially those with disabilities. An ADA toilet typically requires a seat height between 17 and 19 inches from the floor, which helps people transfer in and out without strain. This focus on precise measurements ensures ergonomic design that reduces injury risks and promotes daily independence in commercial spaces.
Let us break down the required toilet height first. For an ADA toilet, the height from the floor to the seat top must be 17-19 inches to accommodate wheelchairs and support easier access. This specification comes from the ADA Accessibility Guidelines, aiming to create equitable environments in public restrooms. Meeting these heights isn’t just about rules; it’s about practical usability that enhances safety for all users.
Moving to a detailed breakdown of toilet dimensions for accessibility, you need at least 60 inches of clear space in front and 56 inches on the side. Grab bars should be 33-36 inches from the floor, providing sturdy support during use. These dimensions work together to prevent accidents and allow for smooth maneuvering, which is crucial in busy settings like offices or stores.
Factors influencing height adjustments can vary by setting, such as older buildings versus new constructions. In homes or small businesses, floor materials might affect how heights are measured, requiring custom installations. Environmental factors, like flooring thickness, could add a half-inch or more, so always account for these to maintain compliance and avoid costly errors.
Practical tips for measuring and verifying dimensions include using a level tool to check heights accurately before installation. Start by measuring from the finished floor to the seat top, ensuring it falls within the 17-19 inch range for an ADA toilet. Double-check side clearances with a tape measure to confirm enough space for wheelchair access, and test grab bar placements for stability.
When dealing with ADA bathroom requirements, procurement challenges often arise, like finding fixtures that match exact standards. Companies such as Foshan Seletti offer certified water closets with customizable heights, making it easier to select products that fit commercial needs without compromising safety. This helps buyers navigate options efficiently, ensuring long-term reliability and cost savings.
A hidden insight is that retrofitting spaces for ADA compliance can involve unexpected costs, such as modifying plumbing or floors to meet height specs. This might mean dealing with structural changes that add time and expense, but planning for adaptable designs can ease future updates. By focusing on flexible solutions now, property owners can handle these challenges more effectively over time.
ADA toilet height requirements also consider user comfort in various contexts, like hospitals where extra support is needed. Knowing how to make a toilet ADA accessible involves integrating these dimensions with other features, such as flush valves at reachable heights. This holistic approach ensures the entire setup works seamlessly for diverse users.
In terms of toilet dimensions, every inch counts for creating inclusive spaces. For example, the overall width should allow for at least 48 inches of maneuverability, supporting full accessibility. These details might seem technical, but they directly impact real-world safety and usability.
Proper ADA toilet dimensions enhance accessibility and safety, helping to minimize risks while supporting everyday use in public facilities.
ADA Toilet Dimension Standards
| Dimension Type | Minimum Height (inches) | Minimum Width (inches) | Required Clear Space (inches) | Compliance Factors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seat Height | 17-19 | N/A | 60 in front | Ensures easy transfer; measured to finished floor |
| Grab Bar Height | 33-36 | 1.5 diameter | 42 length | Supports up to 250 lbs; prevents falls in wet areas |
| Toilet Centerline | N/A | 16-18 from wall | 56 on side | Allows wheelchair access; based on ADAAG |
| Overall Stall Size | N/A | 60 width | 56 depth | Facilitates 360-degree turn; adjusts for doors |
| Flush Valve Placement | 48 from floor | N/A | Easy reach | Must be operable with closed fist; reduces effort |
To wrap up, understanding these key dimensions empowers better design choices that prioritize safety and accessibility. By applying these standards, you can create spaces that meet legal needs and improve user experiences. Remember, accurate measurements and quality products make all the difference in achieving lasting compliance.
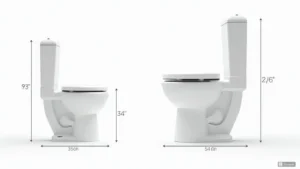

Optimizing Clear Floor Space and Clearances
The ADA outlines specific space needs for toilets to ensure wheelchair users can move freely and safely in restrooms. For an ADA toilet, you need at least 60 inches of clear space in front and 56 inches on one side, allowing for easy transfers and reducing accident risks. These requirements help designers create layouts that promote accessibility without sacrificing functionality in commercial settings.
Let’s cover the minimum clear space first: 60 inches in front ensures enough room for a wheelchair to approach and turn, while 56 inches on one side supports side transfers. This setup follows accessibility standards set by the ADA, making restrooms more inclusive for people with mobility challenges. Proper clearances not only meet legal mandates but also enhance user comfort in everyday use.
In single-user restrooms, best practices for layout planning involve centering the toilet with adequate wall space for grab bars, typically placing them 33-36 inches from the floor. For multi-user facilities, arrange stalls to maximize flow, ensuring each has the required front and side clearances to prevent bottlenecks. This thoughtful design minimizes congestion and supports efficient traffic, especially in high-traffic areas like airports or malls.
The impact of clearances on wheelchair accessibility goes beyond basic movement; it affects how users perform daily tasks without assistance. With proper space, individuals can transfer independently, lowering injury risks and boosting confidence. In contrast, insufficient clearances can lead to awkward positioning, highlighting why precise measurements are vital in ADA-compliant designs.
Real-world case studies show effective space optimization in action, like a hotel retrofit where adding 60-inch front clearance allowed for seamless wheelchair access. Another example is a school restroom redesign that incorporated 56-inch side space, resulting in safer environments for students with disabilities. These successes demonstrate how strategic planning can turn tight spaces into accessible ones, even in budget-limited projects.
When dealing with handicap toilet setups, procurement involves selecting space-efficient fixtures to fit these clearances. Companies like Foshan Seletti offer compact water closet designs that align with ADA standards, helping buyers integrate them without major renovations. This approach addresses supply chain factors, ensuring cost-effective choices that support safety and legal compliance in facility management.
A hidden insight is the challenge of retrofitting older buildings, where structural limits often require costly modifications to achieve the needed space. This might involve shifting walls or updating plumbing, adding to both time and expenses, but focusing on adaptable strategies can make maintenance easier long-term. By anticipating these issues, planners can create more resilient designs that evolve with changing needs.
Space needed for ADA-compliant toilets also intersects with other factors, such as door swings and fixture placement. For instance, ensuring a 32-inch door width complements the 60-inch front clearance, creating a cohesive accessible path. These elements tie into broader accessibility standards, making comprehensive planning essential for full compliance.
While discussing ADA toilet requirements, it’s worth noting how clearances affect overall restroom flow. In multi-user scenarios, optimizing space can reduce wait times and improve hygiene by allowing more room for cleaning. This level of detail ensures that every aspect of design contributes to a safer, more welcoming environment.
Optimizing clear floor space for ADA toilets improves maneuverability and safety, helping users navigate restrooms with ease and confidence.
Clear Space Requirements for ADA Toilets
| Space Type | Minimum Front Clearance (inches) | Minimum Side Clearance (inches) | Key Impact on Accessibility | Compliance Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-User Restroom | 60 | 56 | Allows full wheelchair turn | Measured from toilet front; accounts for door swing |
| Multi-User Stall | 60 | 56 on one side | Facilitates independent transfers | Must include grab bars; prevents overcrowding |
| Wheelchair Approach | 48 width | 56 depth | Supports safe entry and exit | Based on ADAAG; adjusts for obstacles |
| Overall Room Layout | 60 minimum | Variable per setup | Enhances traffic flow | Includes pathways; measured for 360-degree access |
| Retrofit Scenarios | 60 required | 56 adapted | Reduces modification costs | Evaluates existing space; plans for future changes |
In closing, focusing on these clearances leads to better, more inclusive designs that meet ADA standards. By applying these guidelines, you can avoid common pitfalls and create restrooms that serve everyone effectively. Remember, thoughtful optimization today makes for safer spaces tomorrow.
Installing and Securing Grab Bars and Additional Features
The ADA requires grab bars to be installed at specific heights to provide stability and support for users in restrooms. For an ADA toilet, these bars must be placed 33-36 inches above the floor, extending at least 42 inches in length to assist with transfers. This setup enhances safety and independence, making it easier for individuals with disabilities to use facilities without assistance.
Grab bar requirements include not only the height but also the diameter, which should be around 1.25 to 1.5 inches for a comfortable grip. Extensions must reach past the toilet area to offer full support during movement. Following these standards helps prevent falls and ensures long-term reliability in commercial environments.
A step-by-step guide to installing grab bars for ADA compliance starts with selecting the right location, typically 12 inches from the toilet centerline. First, mark the height at 33-36 inches and use anchors suitable for the wall material to secure the bar firmly. Next, test the installation by applying pressure to confirm it holds up to 250 pounds, meeting safety guidelines.
Integrating additional features like flush valves and toilet paper dispensers requires careful coordination. Flush valves should be positioned no higher than 48 inches from the floor for easy reach, while dispensers need to be within 19 inches of the front edge of the toilet. These elements work together to create a fully ADA-compliant setup, improving overall accessibility.
Addressing retrofitting challenges in existing commercial spaces can be tricky, often involving structural changes to walls for proper grab bar mounting. For instance, older buildings might need reinforced backing to support the weight, adding to costs and time. Despite these obstacles, planning with durable components can make the process more efficient and effective.
When focusing on how to make a toilet ADA accessible, procurement decisions play a key role in selecting certified parts. Companies like Foshan Seletti provide durable grab bars and fixtures that meet these standards, offering options that enhance user experience without compromising on quality. This approach supports long-term maintenance goals, ensuring installations remain safe and functional over time.
A hidden insight is that retrofitting often overlooks the need for adaptable designs, such as using modular grab bars that allow for future adjustments. This can help manage ongoing costs and structural modifications, turning potential challenges into sustainable solutions. By emphasizing these strategies, facility managers can maintain compliance more easily as needs evolve.
How to install grab bars for ADA compliance also involves checking for interference with other fixtures, like ensuring clear space around the toilet. In busy settings, such as offices or restaurants, these additions can improve flow and reduce wait times. Ultimately, proper installation contributes to a safer environment for all users.
ADA toilet features extend to details like the placement of soap dispensers, which should be no higher than 48 inches and operable with one hand. Combining these with grab bars creates a cohesive system that promotes independence and reduces injury risks. For an ADA toilet, every feature must align to support seamless daily use.
These technical aspects underscore the importance of precise execution in restroom design. When done correctly, installations not only meet legal requirements but also foster inclusivity in public spaces. Taking the time to follow guidelines ensures that everyone can access facilities comfortably and securely.
Installing grab bars at the correct height improves stability and accessibility, helping users maintain independence in ADA-compliant restrooms.
Grab Bar Installation Standards
| Feature | Height (inches) | Length (inches) | Diameter (inches) | Compliance Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side Grab Bar | 33-36 | 42 | 1.25-1.5 | Supports transfers; must be securely anchored |
| Rear Grab Bar | 33-36 | 36 | 1.25-1.5 | Prevents slips; extends full width behind toilet |
| Flush Valve | Up to 48 | N/A | N/A | Easy operation; integrates with bar placement |
| Toilet Paper Dispenser | 19 from front | N/A | N/A | Within reach; avoids obstruction of space |
| Retrofitting Needs | 33-36 adjusted | Varies | 1.25-1.5 | Assesses wall strength; plans for modifications |
In conclusion, securing these features properly leads to safer, more accessible restrooms that align with ADA standards. By applying this knowledge, you can tackle installations with confidence and precision. Always verify your work to ensure everything functions as intended.
Here’s a summary on achieving and maintaining ADA compliance for toilets and restrooms: The ADA requires standards like proper toilet height (17-19 inches), clear space (at least 60 inches in front), and features like grab bars. Regular inspections every 6 months can help, including checking heights, spaces, and grab bar stability. Document everything with photos and measurements to avoid legal issues. For non-compliance, fix problems quickly, such as adding adjustable fixtures. Long-term strategies include using modular designs and partnering with suppliers like Foshan Seletti for certified products. Key checklist: – Toilet Height: Check every 6 months; avoid below 17 inches. – Clear Space: Annual checks; ensure no obstructions. – Grab Bars: Bi-annual checks; test for stability. By staying proactive, you can create safer, inclusive spaces.
Conclusion
While working at Foshan Seletti, I saw firsthand how critical ADA-compliant restrooms are to creating safer, more comfortable spaces.
As someone who is dedicated to accessible design, I believe these details—like precise heights and clearances—help people with disabilities navigate their daily lives with confidence and ease.
So if you’re embarking on a project, incorporating these guidelines is not only a smart move, it’s a “no-brainer” to promote lasting inclusion.
FAQ
Q1: What is the ADA standard for toilets?
A1: The ADA standard for toilets requires a seat height of 17 to 19 inches for accessibility, along with grab bars on the side and rear walls, clear floor space of at least 60 inches in front, and features like elongated bowls to ensure usability for people with disabilities.
Q2: What are the dimensions of an ADA-compliant toilet?
A2: An ADA-compliant toilet typically has a seat height between 17 and 19 inches, an elongated bowl, and requires at least 60 inches of clear floor space in front and 56 inches on the side for wheelchair access, along with properly placed grab bars.
Q3: What height should an ADA toilet be?
A3: The seat height for an ADA-compliant toilet should be between 17 and 19 inches from the floor to the top of the seat, making it easier for individuals with mobility impairments to use.
Q4: What are the requirements for grab bars in ADA toilets?
A4: Grab bars for ADA toilets must be installed on the rear wall behind the toilet and on the side wall closest to it, with a length of at least 42 inches on the rear and 40 inches on the side, positioned 33 to 36 inches above the floor.
Q5: How much space is needed for an ADA-compliant bathroom?
A5: An ADA-compliant bathroom requires a minimum turning space of 60 inches in diameter, with at least 56 inches of clear space on the side of the toilet and no obstructions within 18 inches of the front, to allow for wheelchair maneuverability.
Q6: What makes a toilet ADA-compliant?
A6: A toilet is ADA-compliant if it meets standards for seat height (17-19 inches), has an elongated bowl, includes side and affair rear grab bars, and is installed with sufficient clear floor space for wheelchair access as outlined in ADA guidelines.
Q7: Are grab bars required for ADA toilets?
A7: Yes, grab bars are required for ADA toilets; they must be on the rear wall (at least 36 inches long) and the side wall (at least 42 inches long), mounted 33 to 36 inches above the floor, to provide support for users.
Q8: What are the flush control requirements for ADA toilets?
A8: Flush controls for ADA toilets must be located on the open side of the toilet within reach (no more than 48 inches from the floor) and operable with one hand, ensuring easy access for people with disabilities.




